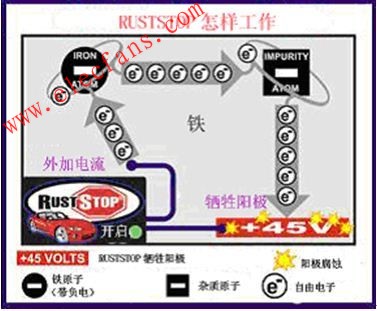
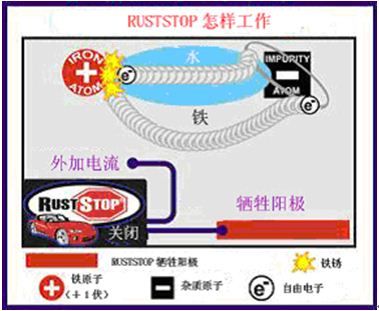
Automotive electronic anti-rust system technology introduction
The automotive electronic anti-rust system is an advanced automobile anti-rust technology that has appeared in the international market for more than a decade. Different from the traditional paint anti-rust, the car electronic anti-rust can prevent rust and rust at the same time inside and outside the car, not only can ensure the body is not It will be damaged by rust, and it can ensure that the main parts of the car will not affect the performance due to rust. Before you get to know the car's electronic anti-rust system, let's take a look at what is electronic rust prevention technology. Electronic rust prevention technology is also known as cathode rust protection technology. Cathodic protection technology is a kind of electrochemical protection technology. The principle is to apply an applied current to the surface of the corroded metal structure, and the protected structure becomes a cathode, so that electron migration caused by metal corrosion is suppressed, and corrosion is avoided or weakened. occur. At present, the cathodic protection technology has matured and is widely applied to the corrosion control of metal structures such as steel pipes, cables, steel wharves, ships, tank bottoms, and coolers in soil, seawater, fresh water, and chemical media. 1834 - Faraday → Cathodic protection principle laid the foundation 1890 - Edison → proposed forced current protection ship 1902 - Cohen → realized Edison's vision 1905 - US for boiler protection 1906 - Germany established A cathodic protection plant in 1913 - named electrochemical protection 1924 - underground pipe network cathodic protection The technology is divided into two types: sacrificial anode cathodic protection and forced current (applied current) cathodic protection. 1) Sacrificial anode cathodic protection technology Sacrificial anode cathodic protection technology is to electrically connect a metal or alloy that is more negative than the metal to be protected to the metal to be protected, and to protect the other by continuously corroding the generated current by the negative metal. metal. Advantages: A: The investment cost is low, and the maintenance cost is basically not required during the operation. B: The utilization of the protection current is high, and there is no over-protection C: No interference to adjacent underground metal facilities, applicable Long-distance pipelines in the plant area and without power supply, and small-scale distributed pipeline protection D: With the function of grounding and protection E: Simple construction technology, no special professional maintenance management is required. Disadvantages: A: Low driving potential, protection current regulation The range is narrow and the protection range is small B: The use range is limited by the soil resistivity, that is, when the soil resistivity is greater than 50 Ω·m, the sacrificial anode protection method C is generally not suitable: in the presence of strong stray current interference area, especially when AC interference occurs. The anode performance may be reversed. C: The effective cathodic protection life is limited by the life of the sacrificial anode and needs to be replaced periodically. 2) Forced current cathodic protection technology The forced current cathodic protection technology is to connect a DC power supply in the circuit, and the auxiliary anode is used to pass the direct current to the protected metal, thereby turning the protected metal into a cathode to protect. Advantages: A: High driving voltage, flexible control of cathodic protection current output over a wide range, suitable for applications with large protection range B: Suitable for use in harsh corrosive conditions or high resistivity environments : Long-term cathodic protection is available when using insoluble or slightly soluble auxiliary anodes D: The protection range of each auxiliary anode bed is large. When the quality of the pipeline anti-corrosion layer is good, the protection range of a cathodic protection station can reach tens of kilometers E: Disadvantages of complete cathodic protection for pipes with poor quality of bare or anti-corrosion layer: A: One-time investment costs are high, and electricity charges are required during operation B: During the operation of the cathodic protection system, strict professional maintenance management is required. C: It is inseparable from the external power supply. It needs to be powered out all the year round. D: It may interfere with the adjacent underground metal structures. Application of electronic anti-rust system in car rust prevention Roche Dow RUSTSTOP first applied sacrificial anode and impressed current technology to electronic anti-rust equipment. Through extensive testing and research, the cathodic protection technology has made great progress, and an improved version of cathodic protection has been realized, which can be sustained. The rust protection is provided under the atmospheric conditions of the electrolyte. This technology - Direct Cathodic Protection (DCP) - cleverly combines sacrificial anode technology with impressed current technology, does not rely on electrolyte (water) to provide a path for free electrons to flow to the anode, but instead adds a current to the protected On the device, electrons are forced to flow through the metal to the positively charged anode. The anodic corrosion (sacrifice), while the corrosion (rusting) process is blocked, so the car is protected. The current that controls the rust of the metal changes as the humidity of the environment changes. If moisture is detected, the risk of rust increases and the system will inject more current to provide greater protection. The instrument outputs a positive volt of 45 volts to the anode. This high voltage makes the attraction of electrons stronger, thus providing stronger rust protection. In addition to direct cathodic protection, these systems also take the form of conventional cathodic protection in wet conditions or in high atmospheric humidity or salt. Even if the dirt and dirt on the equipment are electrically conductive, an electrolyte can be formed to make the conventional cathodic protection effective. The Roche Dopp electronic rust-proof system allows the car to be protected in dry or wet conditions. How does RS-5 work? The RUSTSTOP RS-5 (formerly Rust Stop RS2000) electronic rust preventer successfully combines the impressed current and sacrificial anode technology to effectively overcome the limitations of “conventional cathodic protection†and prevent car rust generation. Rusty is essentially an electrochemical process. The RustStop RS-5 system acts like a “rust magnet†that absorbs electrons that would otherwise rust the car. Then RustStop "corrosion magnet" is corroded, not your car is corroded, letting you see with your own eyes that the system is preventing rust! This chart shows that the RustStop system is off. It can be seen that free electrons react with iron atoms to form rust. Sacrificial Anode: When RustStop is installed, four sacrificial anodes, called "rust magnets" (rust plates), are ordered and connected to the parts of the car where water flow tends to collect or pass. When the RustStop system is turned on, the system command module applies a positive volt of 45 volts to the rust plate (sacrificial anode), causing the iron and impurity atoms to be negatively charged relative to the rust plate. Free electrons are attracted by iron to a rusted plate with 45 volts of positive charge, rather than a negatively charged iron atom. When free electrons reach the rust plate, the plates are corroded (sacrificed). This means that without the RustStop electronic rust preventer, corrosion on the rusted plates can occur on a part of the car. The corrosion of the RustStop rust plate (sacrificial anode) allows you to see with your own eyes that the system is preventing rust. Note: Roche Dow's RustStop RS-5 electronic rust preventer works very well because the output voltage on the rusted plate is stepped up to 45 volts, which creates a larger gap between the car and the rusted plate. The voltage difference makes the rust plate extremely attractive to free electrons, and the whole system works very effectively. Impressed current: The effect of the applied current is that the free electrons in the metal of the car are controlled by the applied current released by the Roststop RS-5 command module. The weak attraction of iron atoms to free electrons is blocked by a strong uniform electron flow (applied current) flowing through the body metal. In short, the constant flow of electrons in the metal prevents the free electrons from reacting with the iron atoms to form rust. The Roststop RS-5 uses the dual technology of sacrificial anode and impressed current, and is the most effective automotive electronic anti-rust system. Novastar LED Display Control System Novastar LED Display Control System,Regular Class B with Novastar,Receiving Card Class B,Led Display Receiving Card Class B Shenzhen Macion Optoelectronics Technology Co.,Ltd. , http://www.macion-led.com