Working principle of disc brake
Working principle of disc brake Most modern cars have disc brakes on the front wheels, and even some cars have disc brakes on all four wheels. It is the part that actually stops the car in the car brake system. Disc brake position The main components of disc brakes include: Brake pad rotor with piston caliper mounted on the hub Parts of disc brakes The moving car has a certain kinetic energy. In order to stop the car, the brake must remove this energy from the car. How does the brake do this? Whenever you stop, the brake converts kinetic energy into heat energy generated by the friction between the pad and the disc. The disc brakes of most cars have vent holes. The single-piston floating caliper disc brake has the functions of automatic center determination and automatic adjustment. Because the caliper can slide from one end to the other, every time the brake is used, the caliper will move to the center position. Similarly, because there is no spring to drag the pad away from the disc, the pad will always have slight contact with the rotor (the rubber piston seal and any sway in the rotor will actually drag the pad to keep it a short distance from the rotor distance). This is important because the diameter of the piston in the brake is much larger than the diameter of the piston in the master cylinder. If the brake piston is retracted into the cylinder, it may be necessary to depress the brake pedal multiple times to draw enough fluid into the brake cylinder to engage the brake pad. Old cars have a dual-piston or four-piston fixed caliper design. One (or two) pistons on each side of the rotor will push the pads on that side. Because the single-piston design is cheaper and more reliable, these two designs have basically been abandoned. On cars with disc brakes on all four wheels, the emergency brake must be activated by a mechanism independent of the main brake when all the main brakes have completely failed. Most cars use cables to activate emergency brakes. Disc brake with parking brake Some other cars have a lever to turn the bolt or start the cam to press the piston of the disc brake. The most common repair to the brake is to replace the pad. Usually, a disc called a “wear indicator†is attached to the disc brake pad. The caliper also has an inspection hole so you can see how much friction material is left on the brake pads. It is not necessary to re-polish every time a brake shoe is replaced. Only when the rotor is deformed or severe scratches appear, it needs to be re-polished. In fact, unnecessary re-grinding of the rotor will shorten its life. Because this process wears away material, the brake rotor becomes thinner after each re-grinding. All brake rotors have a specification for the minimum thickness allowed, and the brake rotor needs to be replaced after the minimum thickness is reached. This specification is provided in the manual of each vehicle. Single Phase Ac Motor,Ac Single Pole Motors,Single Phase Motor,Single Phase Motor Connection Changzhou Sherry International Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.sherry-motor.com
Disc brakes
The most common type of disc brakes installed in modern cars is the single-piston floating caliper disc brake. In this article, we will learn all about the design of this type of disc brake.
This is the position of the disc brake in the car: 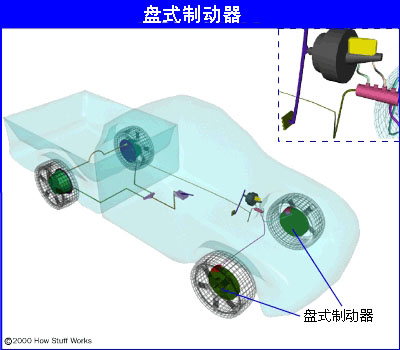

Disc brakes are very similar to brakes on bicycles. The bicycle brake is equipped with a caliper for pressing the brake pad onto the wheel. In disc brakes, the brake pads squeeze the rotor instead of the wheels, and the pressure is transmitted by hydraulic pressure instead of cables. The friction between the pad and the disk will reduce the speed of the disk. 
Ventilation holes for disc brakes
A disc brake with a vent hole has a set of blades on both sides of the disc, which can be used to extract air for cooling. 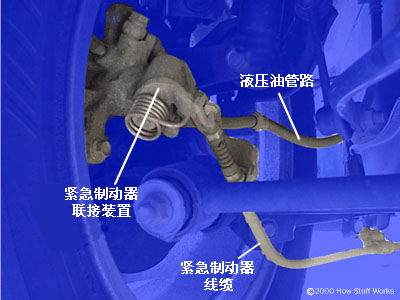
Some cars equipped with four-wheel disc brakes have an independent drum brake in the rear wheel hub. This drum brake is for emergency braking systems only and is only activated via cable; it has no hydraulic system. 
Disc brake pads
When the friction material is worn out, the wear indicator will come into contact with the disc and howl. This means that a new brake pad needs to be replaced. 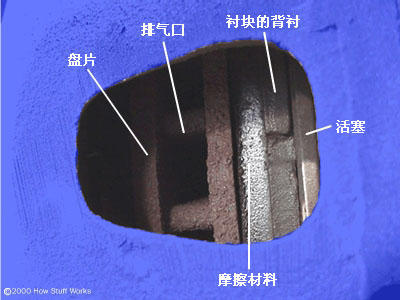
Disc brake inspection hole
Sometimes, there are deep scratches in the brake rotor. This can happen if the worn brake pads remain on the car for too long. The brake rotor will also deform and lose its flatness. If this happens, the brake may shake or vibrate when you stop. Sometimes, these problems can be fixed by re-grinding (also called machining or machining) the rotor. Grinding away some material from both sides of the rotor can restore a flat, smooth surface.