Analysis of MTU principle and related problems
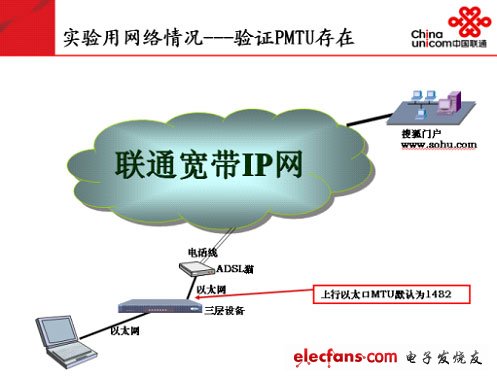
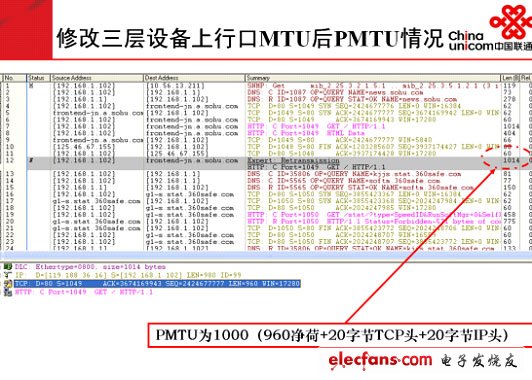
1. Definition of MTU and related concepts: Mtu is the maximum transmission unit, which is called Maximum Transmission Unit, and refers to the maximum packet size (in bytes) that can pass through a certain layer of the communication protocol. Due to the ambiguity of the definition, several related terms, MRU, PMTU, MSS, and JUMBO FRAME are also introduced here for your identification. Second, MTU involves the main principles: 1. MTU value of common network: The IP network transmits information in units of packets. Then, it is one of the core issues to decide how large a packet is and how efficient the packet is. MTU is the de facto standard that determines how many data packets are transmitted on a physical network. Different types of networks have different default values ​​of MTU due to different physical characteristics and development stages. The following are excerpts of various networks and their default MTU value: For the windows operating system, the Ethernet network card MTU defaults to 1500, but it can be modified through the modification tool or the registry, but it can only be changed to small, not large, that is, it can only be modified to less than or equal to 1500 bytes. 2. The PMTU discovery process: For a network-based application, if the MTU and PMTU of the application passing through the network are equal, then the application has the highest efficiency through the network, or the closer the maximum packet sent by the application through the host network card to the PMTU (less than or equal to the PMTU ), The higher the efficiency of the application traversing the network, the reason is to effectively avoid fragmentation and reorganization. In order to achieve this goal, some operating systems support the function of automatically discovering the path MTU. The specific process is: A packet with a packet length greater than the MTU value of the interface is received on the router interface. If the packet is marked as non-fragmented, the packet will be discarded and an ICMP error packet will be returned to notify the packet initiator to discard the reason. The message initiator will send a smaller message. Through multiple negotiation of the above messages, the minimum Mtu value for a certain fixed path will be obtained. This process is called "Mtu Discovery" [see RFC1191] for details. Understand the principle of MTU discovery, give an example to verify the change process of PMTU: In the experimental network shown in the figure above, the PPPOE dial-up is simulated by the three-layer equipment to achieve access to the broadband IP network. The default MTU of the upstream Ethernet port of a Layer 3 device is 1482 bytes. The packet capture results are displayed as follows: Change the default MTU of the upstream Ethernet port of the Layer 3 device to 1000 bytes. The packet capture results are displayed as follows: 3. "PMTU" found the existing problems: Due to the inability to standardize the configuration of routers or other network devices on the Internet, some operators or websites take into account network security and other needs, and sometimes filter out ICMP messages. In addition, PMTU involves hosts, various switches, and routers , Firewalls and other network devices, these hosts and network devices have no effective means to achieve PMTU negotiation and interaction, so that Mtu Discovery cannot run normally, affecting the normal operation of applications, that is, there is currently no effective means to discover PMTU. When a network device on the Internet encounters MTU discovery packets or must fragment IP packets but DF is set to 1, the router can use any of the following methods (excerpt from the Internet): Send the "ICMP DesTInaTIon Unreachable-FragmentaTIon Needed and DF Set" message that originally defined in RFC 792, and then discard the packet. The original message format does not contain information about the IP MTU of the link that failed to forward. (Causes PMTU cannot be found normally) ? Send the "ICMP DesTInation Unreachable-Fragmentation Needed and DF Set" message that is redefined in RFC 1191, and then discard the packet. This new message format contains an MTU field that indicates the IP MTU of the link that failed to forward. (PMTU may be found normally) RFC 1191 defines path MTU (PMTU) discovery, which enables source and destination TCP peers to dynamically discover the IP MTU of a path between the two, thereby discovering the TCP MSS of that path. Once it receives the "Destination Unreachable-Fragmentation Needed and DF Set" message defined by RFC 1191, TCP will adjust the MSS of the connection to the specified IP MTU minus the size of the TCP and IP headers. In this way, subsequent packets sent on this TCP connection will not exceed the maximum size and can be transmitted on this path without fragmentation. Discard the packet directly. A router that directly discards packets that need to be fragmented but whose DF flag is set to 1 is called a PMTU black hole router. In short, the undiscoverable nature of PMTU causes the application system to fail to run normally due to MTU problems.
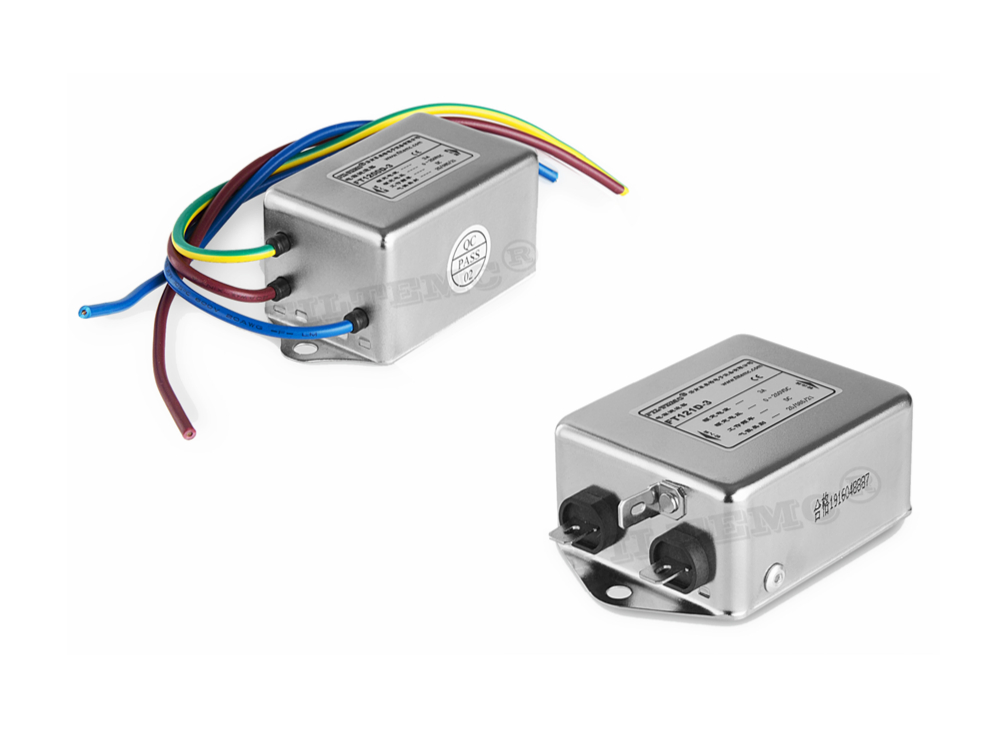
Technical Data of DC RFI Filter
Rated current of DC EMI Filter: 0.5A~2000A
Features of DC Line Filter
High performance DC filters with exceptional common and differential mode filtering effectfor interference from 10KHz to 30MHz.
FT121D series are two-stage common mode filters
High voltage versions above 250VDC are also available upon request.
Suitable for switch power supply, SPC exchange and other DC electric device.
DC EMI Filter DC EMI Filter,DC RFI Filter,DC Line Filter,DC Noise Filter Jinan Filtemc Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.chinaemifilter.com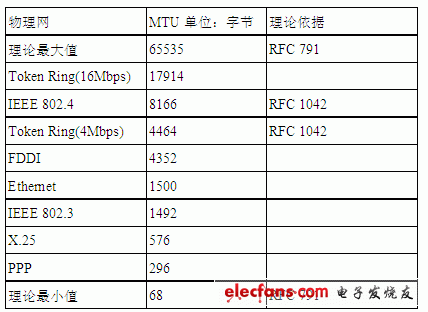

Working voltage: 0~250VDC
Various connection types: wire, solder lug, stud
Custom specific versions on request
